Understanding Paid Search Engine Marketing
Definition: Paid search engine marketing (also known as PPC or pay-per-click advertising) is a digital strategy where businesses pay to have their ads displayed on search engine results pages (SERPs) in response to specific keywords. This form of advertising targets users who are actively searching for products, services, or solutions—making it one of the most effective ways to capture high-intent traffic and generate measurable results quickly.
Paid search allows for keyword-level targeting, real-time performance tracking, and budget control—making it ideal for startups and growth-focused brands looking to accelerate visibility and conversions.
Use in a Sentence: We launched a paid search engine marketing campaign targeting high-converting keywords and saw a 45% increase in qualified traffic within two weeks.
Benefits of Effective Paid Search Engine Marketing
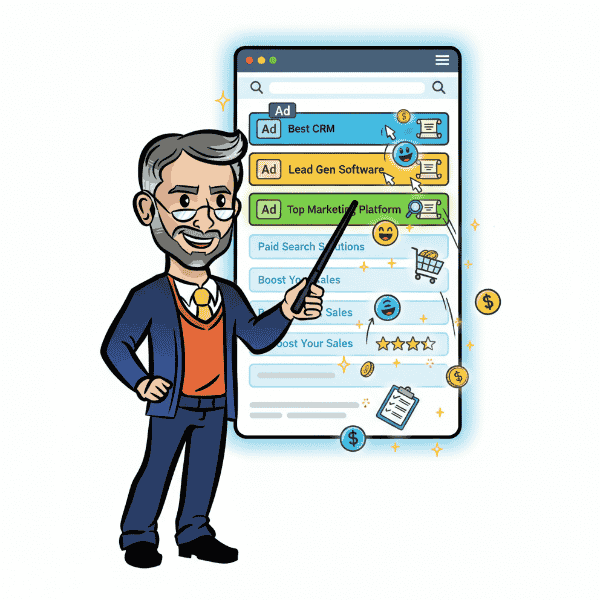
- Immediate Visibility: Appear at the top of search engine results pages (SERPs) the moment your campaign goes live, putting your offer in front of people who are actively looking for it.
- Targeted Traffic: Reach users based on intent by bidding on keywords that match exactly what your ideal customer is searching for.
- Scalable and Flexible: Whether you’re working with a small budget or scaling up, paid search campaigns can be adjusted in real-time to meet your goals.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Every click, impression, and conversion is trackable, allowing you to continuously refine campaigns based on real-time performance.
- Outperform Competitors: With smart bidding strategies and compelling ad copy, you can outrank competitors and win attention in crowded markets.
Key Elements of Paid Search Engine Marketing
- Keyword Strategy: Start with a solid keyword plan. Identify high-intent terms your audience is already searching for and build ad groups around them.
- Ad Copy & Extensions: Write clear, benefit-driven ads with compelling calls to action. Use ad extensions (like sitelinks and callouts) to boost visibility and relevance.
- Landing Page Relevance: Make sure your ads lead to fast, mobile-friendly pages that match the user’s search intent. This improves both conversion rate and Quality Score.
- Budget & Bidding: Set a realistic daily budget and choose the right bidding strategy—manual CPC, target ROAS, or maximize conversions—based on your goals.
- Tracking & Optimization: Use conversion tracking, UTM parameters, and A/B testing to analyze performance and refine your campaigns over time.
- Remarketing Strategy: Re-engage past website visitors with tailored search ads that bring them back to complete their journey.
More Definitions
(From the Sales & Marketing Jargon Encyclopedia)
- Qualified Lead: A prospect who meets certain criteria and demonstrates intent or potential to become a customer.
Read More> - Link Juice: The SEO value or authority passed through hyperlinks to boost search rankings.
Read More> - One and Done: A sales or marketing approach that lacks follow-up or nurturing—often ineffective.
Read More>
Useful Posts
(From the Sales Funnel Professor Blog)
- Top of Funnel: Organic Social Strategies: Learn how to build brand awareness using unpaid social media content and outreach.
Read More> - SEO Top of Funnel Strategies: Dive into organic tactics that increase visibility at the awareness stage without a paid budget.
Read More> - How to Find Low-Hanging Fruit in Sales & Marketing: Discover practical ways to identify quick wins and easy-to-implement strategies that don’t require a big spend.
Read More>







![Cartoon illustration of a professor standing next to an unused, generic megaphone while presenting a customized digital message reading "Hello, [Name]!" to a single customer figure, symbolizing a personalized campaign strategy.](https://salesfunnelprofessor.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/personalized-campaigns-definition.jpg)